Change Management
Resistance is a rational response to an ERP implementation ...
… even for the “A-Team.” Understanding why is the key to effective change management.
- Autonomy is a fundamental psychological need. By nature, ERP systems diminish autonomy.
- Competence is another psychological need, and ERP systems can turn someone who was an expert yesterday into a novice tomorrow.
- The feeling that other people care about them is another basic psychological need (relatedness), and a careless ERP implementation can make people feel that the organization does not care about them.

Getting the right things right

ERP systems represent transformational change.
Everyone should know that change management involves communication and training. Post implementation surveys always cite this. ADKAR, the de-facto standard framework for change management, is vastly better than not using a change management framwork. But ADKAR has some significant shortcomings.
Research for the Eight Pillars project revealed the need to significantly augment ADKAR to directly address the three basic psychological needs for intrinsic motivation above (autonomy, relatedness, and competence (ARC)), resulting in the ARC Motivational Framework for ERP Transformation. ADKAR + ARC = Getting the Right Things Right.
Navigating Change Management
ADKAR and the Need to Go Beyond a “Checklist” Mentality.
Elements of ADKAR:
- Awareness
- Desire
- Knowledge
- Ability
- Reinforcement
I think of ADKAR this way:
Motivation
Surely the psychologists at Prosci understand the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation (desire). ADKAR contributes to both, but understanding the difference between them is critical in the application (or misapplication) of ADKAR, and ADKAR does little to clarify this.
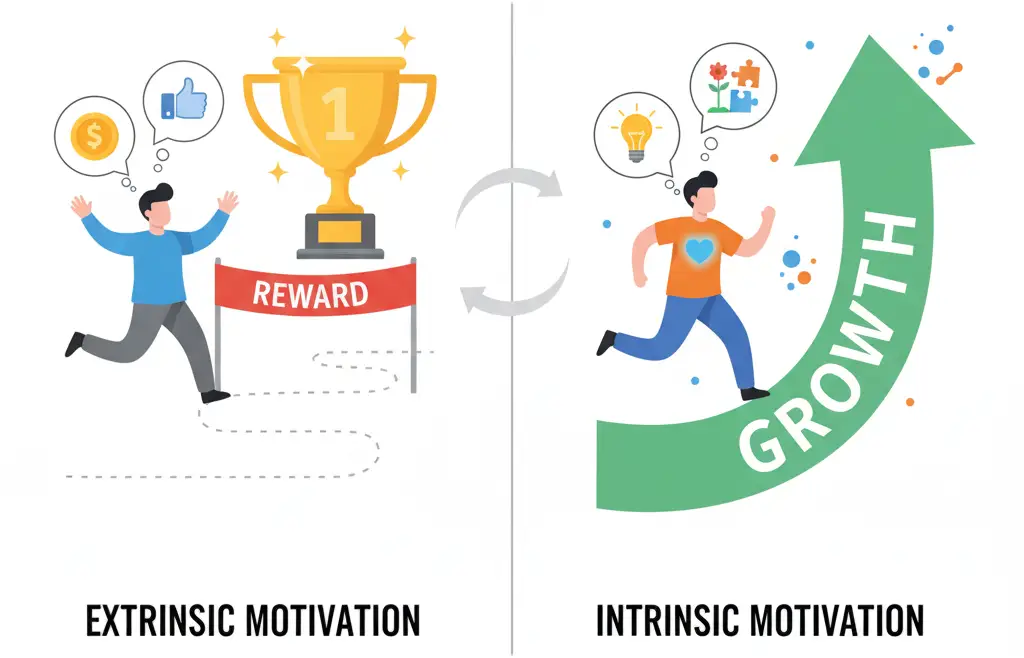
Extrinsic Motivation
Is the desire to do something because of an external reward (an incentive), or to avoid a punishment.
Intrinsic Motivation
Is the desire to do something for its own sake because you find it enjoyable or fulfilling.
Importantly, Intrinsic motivation drives employee engagement, and extrinsic motivation can damage intrinsic motivation.
Desire: The Bedrock of the Change Bridge
ERP Systems are Inertently Damaging to Intrinsic Motivation
Because it’s the key to unlocking employee engagement, let’s dig into intrinsic motivation a little more. Arguably the leading, and most empirically supported theory of intrinsic motivation is Self-Determination Theory (SDT) It’s a foundational theory that has shaped the field of motivation for decades. Daniel Pink based his bestselling book “Drive” on Self-Determination Theory.
Think of intrinsic motivation as a fire. Self-Determination Theory identifies the three essential “nutrients” that fire needs to burn brightly. If any of them are missing, the fire of motivation will diminish or go out.
I went back to school to get a degree in Industrial-Organizational Psychology to understand why change management in ERP implementations is so hard. What I learned is that ERP implementations typically damage all three nutrients that feed the fire of intrinsic motivation:
Autonomy
- Lack of Involvement
- Standardization
- Reduced Problem Solving
- Decision-Making
- Loss of Personal Tools
- Increased Scrutiny
Competence
- Turns Experts into Noivces
- Drop in Productivity
- Unforgiving Systems
- Inadequate Training
- Confusing Error Messages
Relatedness
- "No One Cared to Ask Me"
- Disrupted Social Connections
- Focus on Data, Not People
- "Super Users" vs. "End Users"
- IT vs Business
- Generational Divides
The Good News ...
… is that once we know the issues, we can address them.
Compliance is the Minimum, Engagement is the Goal
Engagement is the Goal
Extrinsic vs intrinsic motivation is the difference between compliance (the minimum), and engagement. The stakes are high, and there is a vast difference.
Engagement is the holy grail of worker motivation.
Compliance
Engagement
The “Why”
“I have to”
“I want to”
Motivation
External
(reward & punishment)
Internal
(pursues purpose)
Focus
Rules and policies
Goals and mission
Results
Meets standards
Exceeds standards
Outcome
Stability
Growth, innovation, higher productivity
The ARC Motivational Framework for ERP Transformation
The ARC Framework for ERP Change
This motivational gap is addressed with my proprietary ARC Framework for ERP Change, a strategic extension to ADKAR grounded in the science of Self-Determination Theory (SDT), the motivational theory behind the New York Times #1 Bestseller “Drive: the Surprising Truth Behind What Motivates People”
The ARC framework is built on the principle that genuine engagement comes from satisfying the three universal psychological needs that drive all human motivation:
- Autonomy: The need to feel a sense of choice and control.
- Relatedness: The need to feel connected to others and a sense of belonging.
- Competence: The need to feel effective and masterful in one’s work.
ADKAR + ARC
By blending ADKAR with ARC strategies, change management is transformed from a top-down mandate into a human-centric practice. It goes beyond managing change; building the conditions for your team to embrace the change.
Awareness
Objective | Hidden Threat | ARC Enhanced Strategy |
Communicate the need for change. | Relatedness | Build Relatedness |
Desire
Objective | Hidden Threat | ARC Enhanced Strategy |
Foster the personal choice to support the change. | Autonomy, Relatedness & Competence | Continuous, Intentional ARC Diligence |
Knowledge
Objective | Hidden Threat | ARC Enhanced Strategy |
Provide training on how to change. | Competence | Meaningful Competence |
Ability
Objective | Hidden Threat | ARC Enhanced Strategy |
Ensure individuals can implement the change. | Competence & Autonomy | Foster Mastery and Ownership |
Reinforcement
Objective | Hidden Threat | ARC Enhanced Strategy |
Make the change stick. | Autonomy | Reinforce through Intrinsic Satisfaction: Publicly recognize and celebrate adoption (Competence), collaborative wins (Relatedness), and stories of how the new system creates organizational impact (Autonomy). |
The ARC Advantage: From Compliance to Engagement
The integrated ARC-ADKAR approach turns a major risk, user resistance, int. The result is a set of tangible business outcomes:
- Increased User Adoption: Engaged employees use the system more effectively and consistently, unlocking its full potential.
- Accelerated ROI: High adoption and proficiency mean you realize the promised business benefits faster.
- Reduced Employee Turnover: Supporting your team’s psychological needs reduces burnout and retains critical talent.
- A Change-Ready Culture: We build your organization’s “change muscle,” creating a more resilient and adaptive culture for future challenges.
The Taxonomy of Change Management Success
Getting Change Management right requires getting a hierarchy of things right. Explore the taxonomy of Change Management critical success factors below. Click the grey + to reveal more detail.
- Change Management
- Strategic Alignment & Leadership
- Leadership Commitment & Vision
- Executive Sponsorship
- Defined "Why"
- Modeling Behaviors and Commitment
- Integrating OCM into Business Strategy
- Framing ERP as a Business Transformation
- Prioritizing & Resourcing OCM from the Outset
- Communicating Success Criteria
- Organizational Readiness
- Cultural & Behavioral Assessment
- Assessing Cultural Readiness
- Managing the Human-Centric Shift
- Operating Model & Process Alignment
- Redesigning Business Processes (BPR)
- Aligning Roles, Responsibilities & Performance Metrics
- Stakeholder Engagement & Communication
- Strategic Communication
- Comprehensive Communication Plan
- Consistent, Multi- Channel Messaging
- What's In it For Me (WIIFM) Communication
- Stakeholder & User Participation
- Early & Continuous User Involvement
- Feedback Mechanisms
- Empowering Users to Influence Outcomes
- Workforce Enablement & Support
- Training Strategy & Design
- Developing a Comprehensive, Resourced Training Plan
- Role-Based & Process Oriented Curriculum
- Blended Learning Approach
- Training Delivery & Execution
- Providing Hands-On, "Just-in-Time" Training
- Real-World Scenarios & Data
- "Train-the-Trainer"
- Post-Go-Live Support
- Post-Go-Live Support Plan
- Continuous Training & Capability Building
- Accessible Support Resources
- Adoption, Behavior & Resistance Management
- Understanding & Managing Attitudes
- Proactively Managing Employee Attitudes & Concerns
- Focus on User Experience
- Driving Adoption & Behavior Change
- Behavior Change Beyond Communication
- Behavioral Science & Social Influence
- Proactive Resistance Management
- Anticipating & Mitigating Resistance
- Addressing Root Causes with Empathy
- Preventing & Managing Workarounds
- OCM Governance & Execution
- OCM Structure & Methodology
- Structured Change Management Methodology
- Building a Skilled, Cross-Functional OCM Team
- Change Champion Network
- OCM Measurement & Analytics
- Defining & Tracking Metrics
- Using Data to Tailor Interventions
- Measuring Training Effectiveness & Employee Satisfaction